Hair Color Wheel: How To Use It When You Dye Your Hair
This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission, at no cost to you, if you make a purchase.
In your favorite beauty store, you came across a boxed hair dye showing a model with this beautiful hair.
Oh, I’d like to try that color! You think to yourself.
You bought that dye and used it at home.
After dyeing your hair, you checked the results in the mirror, and guess what? You’re seeing a color that’s far from what the model on the box has!
But you followed the instructions, so what did you do wrong?
How come hairdressers can always give you the color you want? Is it because they use professional dyes? Do they have a magic trick?
Want to know their secret? It’s the hair color wheel!
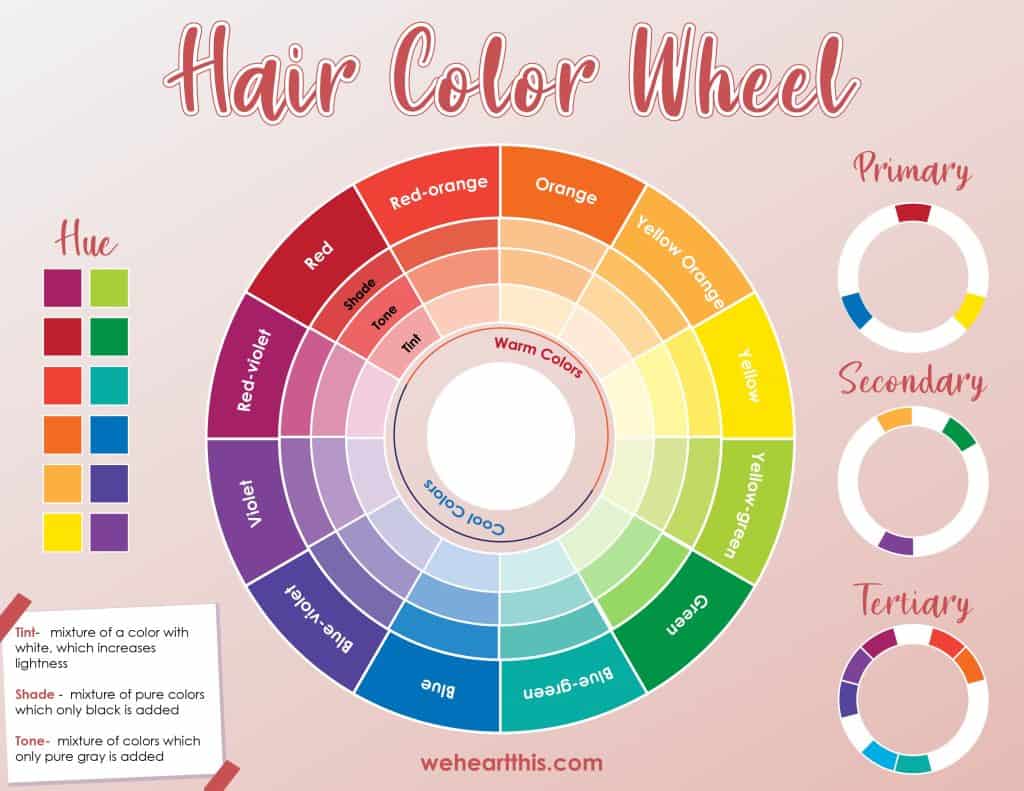
This is a hair colorist’s powerful tool to give us the perfect color and the most flattering shade for our skin tone. Understanding the hair color wheel helps you make sure that your dye looks good and stays that way.
And today, we’re ready to reveal this mystery to you!
Table of Contents
What Is the Hair Color Wheel?
The color wheel for hair coloring is literally a wheel that sometimes even looks like a hair color wheel spinner.
It usually has 12 colors: 3 primary, 3 secondary, and 6 tertiary. The colors are divided into warm and cool tones.
Most hair color wheels are customized with numbers to make shade combinations easier, while some charts even have additional hair levels and undertones.
This tool gives stylists an effective way of formulating the best colors for their clients.
How Does a Color Wheel Work for Hair?
The color wheel makes use of the color theory.
Its main purpose is to help artists — painters, designers, colorists — understand the relationship of colors.
When hair dyeing, stylists use their knowledge of the color wheel chart in hairdressing to do the following:
- Combine shades
- Counteract unwanted tones on your hair
- Enhance certain tones in the hair
Because of this amazing instrument, your hairdresser can work out how to achieve the color you want.
The Hair Color Theory
Put on your lab coat because we’re going to talk about the science of colors!
Color theory is the study of how colors work. It shows what happens when you combine certain colors or when you remove a hue from a color, based on the color wheel.
Hairstylists also use this science when it comes to hair coloring.
In the hair color theory, stylists use the color wheel to determine which colors complement each other and which colors to mix to get a specific shade.
Allow us to give you an overview of how this system works.
To understand how professionals do it, we’ll learn about hue, hair level, and color intensity. We’ll also explain complementary colors.
Hue
It’s easy to use the word “hue” as a replacement for “color,” but did you know that it has a different meaning?
Color is a general term for shade, tint, or hue. Whereas hue specifically refers to the color’s family.
For example, we can say that burgundy is a color that has a red hue.

Level
You might have heard your stylist say this word whenever you ask for a color, especially when you’re asking to go blonde.
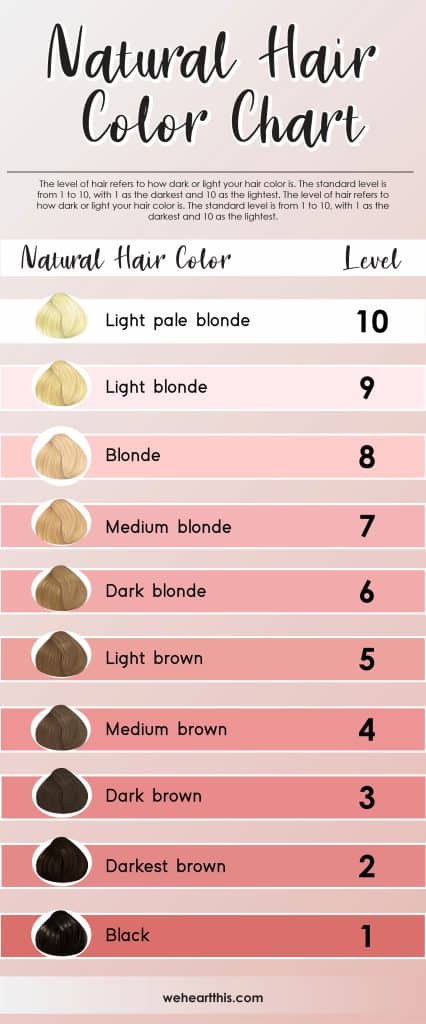
The level of hair refers to how dark or light your hair color is. The standard level is from 1 to 10, with 1 as the darkest and 10 as the lightest.
| Natural Hair Color | Level |
|---|---|
| Light pale blonde | 10 |
| Light blonde | 9 |
| Light blonde | 8 |
| Medium blonde | 7 |
| Dark blonde | 6 |
| Light brown | 5 |
| Medium brown | 4 |
| Dark brown | 3 |
| Darkest brown | 2 |
| Black | 1 |
Intensity
We’ve seen hair with bright colors. We’re also familiar with pale or pastel hair.
This variation is affected by what we call intensity, which is the strength of color. Another word for intensity is saturation.
Color is most intense in its pure form. You can make it darker or lighter by adding black or white.
Complementary Colors
Colors that are placed on opposite sides of the color wheel are complementary.
The first thing to note about complementary colors is that when you put them next to each other, they pop. That’s because a pair of complementary colors is made up of one cool tone and one warm tone, creating contrast.
So when you want to highlight your eye color, you can choose a hair shade that complements your eyes.
Additionally, colors that complement also cancel each other out.
What does it mean?
When you mix these hues, each loses its effect and becomes a neutral or natural color, like brown, gray, or even white.
What if you‘ve already colored your hair before reading this post, and now you have a hair color you’re not proud of?
If you want to fix a bad dye job, use the complementary colors of the hair color wheel for color correction.
For instance, your color application resulted in muddy green hair. You can get rid of that nasty green by using a red dye.
That’s because red is opposite to green in the hair color chart, so they’ll neutralize each other and turn into ash or brown.
Formulating Hair Color Using the Color Wheel
Now that we know about the essential terms in the color theory, how will this affect the mixing of hair dye?

Let’s go back to what we said earlier about having a hair dye result that’s far from what’s shown on the box.
Why is it difficult for you to get the exact shade while professional colorists can do it?
That’s because they don’t simply let you pick a color and apply that shade to your hair. They have many things to consider to guarantee that you’ll get the hair you want.
Here are the factors:
- Your existing color
- Your desired color
- Whether you are going darker or lighter
Using the color wheel, a stylist can determine which shades to add to their formula so they can deliver your expected result.
Let’s say you want to dye your hair a beautiful ash brown shade. Your hairstylist won’t just get a product that’s labeled “ash brown” and use it on you.
If you have copper hair, your stylist will use an ash blue dye to give you the ash brown that you want.
That’s because according to the color wheel, blue can cancel out your copper’s orange hue, and therefore give you a neutral brown color.
Using the Color Wheel When You Dye Your Hair at Home
With lots of color-related terms in the color theory, it can be intimidating to use a hair color wheel. But you don’t have to be an artist to use it.

In fact, you can use this tool or the color theory we’ve explained above for you to get the best out of your DIY hair dye.
Pick the Right Shade
The hair color wheel can help you find the shade that flatters your skin tone.
Before we proceed, you have to identify your undertone first. Here are the things that you can do to find out your skin’s undertone.
Look at your wrist’s veins.
- Cool — Your veins appear to be blue or purple.
- Warm — They’re green.
- Neutral — Your veins are either a mix of blue and green or colorless.
Put on both gold and silver jewelry.
- Cool — Silver looks flattering.
- Warm — Gold looks better on you.
- Neutral — Both gold and silver look good.
Put on a white shirt and go outside in the daytime.
- Cool — Your skin looks pinkish.
- Warm — Your skin looks yellowish.
- Neutral — You look good in white.
Now, to find the most flattering shade, remember these notes.
Warm hair colors like auburn, copper, or golden blonde look best on people with warm undertones.
On the other hand, those who are cool skin-toned may choose hair dyes in cool shades such as lilac or ash blonde.
With neutral undertones, well, you’re in luck because any shade can complement your skin tone.
Hair Toning Color Wheel
Speaking of neutralizing, can you use a color wheel for hair toners?
Yes. A hair color wheel can help you choose which hair toner you should use.
Yellow Tones
If your light blonde or silver hair starts to turn yellow, you can use a purple toning shampoo to remove the unwanted yellow tone.
For this, we recommend L’Oreal Paris Ever Pure Purple Shampoo. It’s sulfate-free and effective in neutralizing brassy yellow tones in your hair.
Orange Tones
For dark blondes or brunettes who bleached their hair and ended up with rusty locks, a blue-based toner can be used.
Let me repeat that: blue-based. There may be some people complaining that the purple shampoo they used didn’t get rid of their hair’s brassiness.
And what do they have in common? They have orange hair, not yellow.
That’s why knowing the color wheel is important. You need to use the actual shade that would neutralize the color effectively.
That said, the best blue toner for us is Matrix Total Results Brass Off Blue Shampoo. It neutralizes brassy tones in lightened brunettes.
Red Tones
Usually, people with medium to dark brown hair end up having red tones, even if they don’t bleach. This is because the underlying pigment in these shades of brown is red.
The red pigment can be exposed when their locks have dried out from shampoo, have too much sun exposure, or have been soaked at the beach.
If you’re one of them and you want the red tones gone, you can use a green-based toner.
There are lots of green toners available, but our favorite is Keracolor Color + Clenditioner because it not only deposits pigment, it also cleanses and conditions.

Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know my hair level?
To know your hair level, simply grab a section of your hair and hold it out where you can see it. Then match what you see with the closest number in the hair level chart.
Is there a natural hair color wheel?
There’s no natural hair color wheel, but there is a natural hair color chart that you can easily find online.
This hair color chart shows four natural colors: blonde, brown, red, and black. These colors can vary in tone and intensity.
Get Your Dream Color
Whether you plan to DIY or let professionals do their job, you can have a gorgeous shade that suits you.
Before you dye or tone your hair, try to study the color wheel and color theory. Remember the colors that you can mix to enhance each other and the colors that can cancel one another out.
This way, you can formulate the best shade for your hair.
Don’t just look at photos of beautiful colored hair. Go ahead and get it!

Thinking of beautiful hair colors?
Look at these hair dye ideas:


